Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in human-level reasoning as well as generation in the past few years. They are widely used in a wide range of applications such as text generation and summarization, completing sentences, translating documents, and many others. Given their wide spectrum of use cases, a team of researchers from Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab, The University of Hong Kong, and The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology have started exploring their application in mathematical problem-solving, and this research paper talks about leveraging LLMs to do so, more particularly to tackle geometric problems.
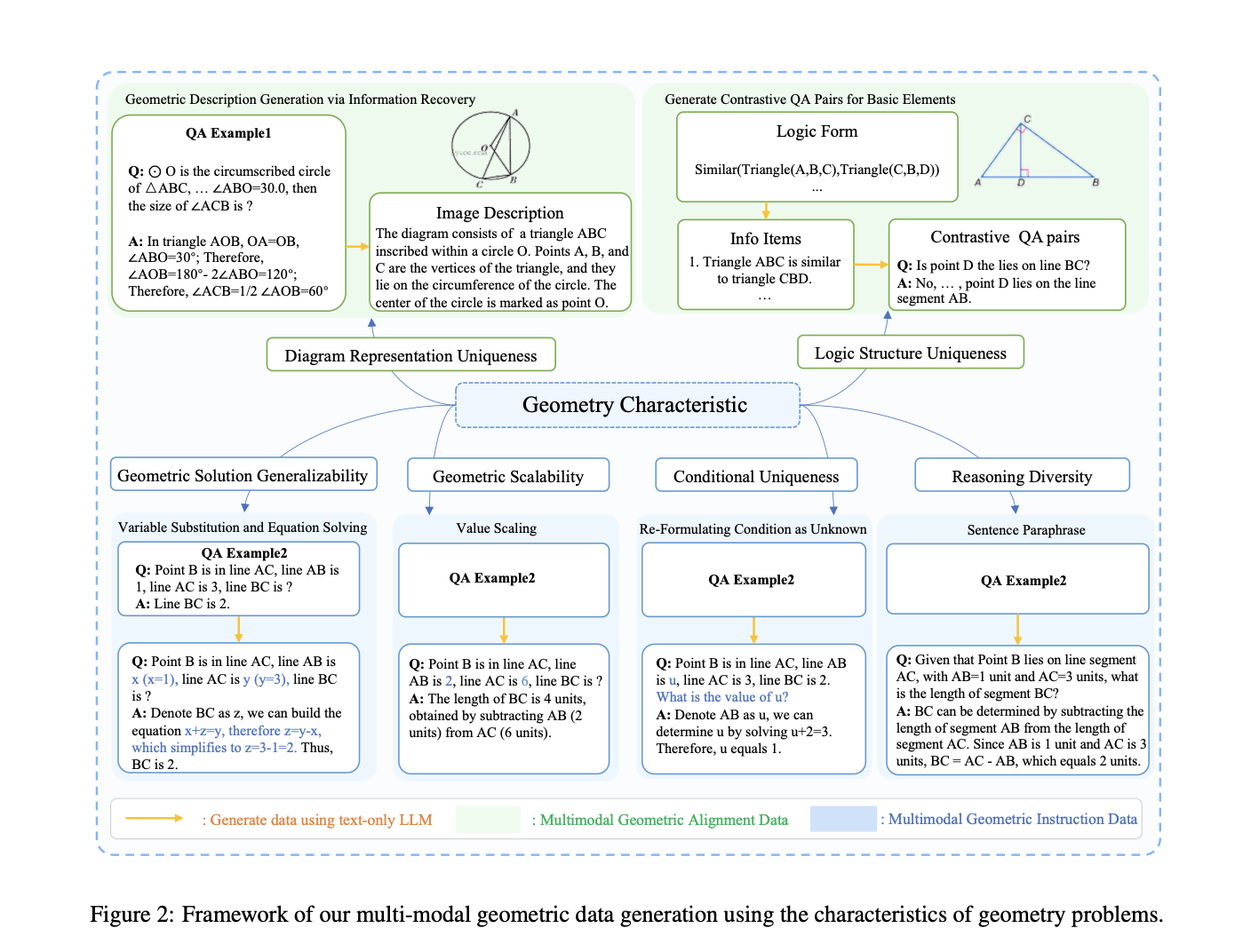
Although much research has been done on using LLMs to solve mathematical questions, it mainly focuses on text-based problems, not those involving geometrical information. The latter involves accurately comprehending geometric figures, which the current models show limitations in, and to bridge this gap, the authors of this research paper have introduced a multimodal geometry dataset called Geo170K and a model named G-LLaVA, which utilizes the same and is highly capable of solving geometric problems.
Many state-of-the-art multimodal large language models (MLLMs) suffer from hallucinations when it comes to solving geometric problems, which greatly affects their abilities. One of the reasons for this is the lack of a descriptive dataset, and to address this issue, the researchers have created Geo170K consisting of thousands of geometric image-caption and question-answer pairs. The dataset consists of detailed descriptions of geometric images and diverse problem-solving methodologies, which allows MLLMs to understand fundamental geometry concepts and user instructions to generate accurate geometry solutions.
The research team developed G-LLaVA, an MLLM that has been derived from the Geo170K dataset, which makes it highly proficient in solving geometric problems. As the name suggests, the LLAVA architecture has been used in the design of the model, and the model primarily consists of an LLM and a trained vision transformer (ViT). Moreover, the model has been trained in two phases – geometric visual-language alignment and geometric instruction-tuning. The dataset, along with the model architecture, makes G-LLaVA an exceptional tool to solve geometric challenges, significantly outperforming many state-of-the-art MLLMs even with lesser parameters.
For evaluation, the researchers compared the performance of their model with other MLLMs on the MathVista benchmark. The results demonstrate the model’s exceptional performance, where it outperformed even models like GPT4-V and Gemini Ultra. G-LLaVA-13B achieved an impressive accuracy of 56.7% compared to the other two models, which achieved a score of 50.5% and 56.3%, respectively. Moreover, the researchers also compared G-LLaVA with other baseline models on different types of questions, such as angle, length, and area problems, and the model performed better than the others on all kinds of questions.
In conclusion, the researchers have tried to address the limitations of current MLLMs when it comes to solving geometric problems. They have first created a comprehensive and diverse dataset that allows G-LLaVA to gain an understanding of fundamental geometry concepts, and it guides the model in better answering user questions. The model showed remarkable capabilities and even outperformed GPT4-V on the MathVista benchmark with just 7B parameters. The researchers hope that their work will help in future research and eventually improve the geometric problem-solving abilities of MLLMs.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to join our 34k+ ML SubReddit, 41k+ Facebook Community, Discord Channel, and Email Newsletter, where we share the latest AI research news, cool AI projects, and more.
If you like our work, you will love our newsletter..
Asif Razzaq is the CEO of Marktechpost Media Inc.. As a visionary entrepreneur and engineer, Asif is committed to harnessing the potential of Artificial Intelligence for social good. His most recent endeavor is the launch of an Artificial Intelligence Media Platform, Marktechpost, which stands out for its in-depth coverage of machine learning and deep learning news that is both technically sound and easily understandable by a wide audience. The platform boasts of over 2 million monthly views, illustrating its popularity among audiences.